Non Oversampling: How to Achieve the Best Audio Quality

Non-oversampling (NOS) is a digital-to-analog conversion (DAC) process that skips the interpolation or oversampling process. It is commonly used in new models of digital audio systems. Instead of upscaling the digital audio signal, a Non-oversampling (NOS) DAC processes the signal directly at its native resolution and sample rate.
Check Out: Best Non-Oversampling (NOS) DACs Under $200 2025
What is Non Oversampling (NOS) and How Does it Work?
A non oversampling (NOS) is a digital-to-analog conversion (DAC) process that skips the interpolation or oversampling process. It is commonly used in new models of digital audio systems. Instead of upscaling the digital audio signal, a non oversampling (NOS) DAC processes the signal directly at its native resolution and sample rate.
A Non-Oversampling (NOS) DAC converts digital audio signals directly into analog signals without altering the original sample rate or bit depth.
Here are some methods on how Non-Oversampling DAC works
1. Direct Signal Processing
Non-oversampling DAC receives the digital audio signal and converts it into the same bit rate as a standard sample rate, like 44.1 kHz or 48 kHz, is fed directly to the DAC.
On the other hand, oversampling DACs, which interpolate additional data points between existing samples, a NOS DAC processes only the original samples.
2. Conversion to Analog
Next is the conversion to analog
The Non-oversampling DAC receives the digital signal and is passed through a digital-to-analog converter chip, where each digital sample is transformed into an analog voltage level.
This results in a “stepped” waveform representing the original audio signal.
3. Analog Smoothing
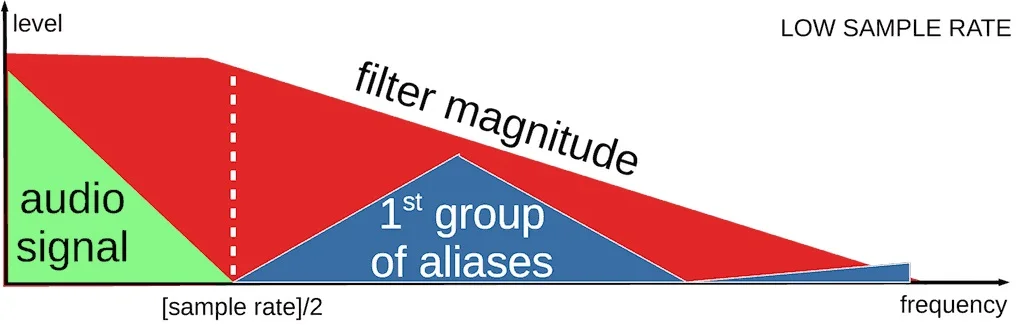
To improve the stepped waveform and cut off any excessively high-frequency components (for instance, aliasing noise), a low-order analog filter is put in place.
While oversampling DACs tend to depend on digital filters, NOS DACs (non oversampling) prefer using analog filters for style and quality purposes, at times neglecting complexity.
Primary Attributes of Non-Oversampling (NOS) – non oversampling DACs
The first one is Direct Conversion – Direct Conversion non oversampling (NOS) DACs do not change the sample rate or the bit rate depth of the original audio file, so the output audio signals retain the original sampling data.
Simplicity- This utilizes simple designs, thus fewer steps in digital processing or signal tweaking. Depends on the design.
No Digital Filtering- For non oversampling DACs, they skip the digital filter, which is considered essential in oversampling systems.
Focus on Signal – The concentration is the analog filter path and unadulterated signal.
What is an NOS DAC?
An example of a digital-to-analog converter NOS DAC is an Non non oversampling DAC, which does not contain an oversampler and at times, does not even contain an analog filter. Unlike standard DACs that upsample digital audio signals to a higher rate for processing, NOS DACs do not use any digital interpolation, and audio signals are processed at the original sample rate and bit depth.
The goal of this guide is to introduce and explain the fundamentals of NOS technology and its application in audio systems. Learn more below on why the NOS digital-to-analog converters are used, classifications, benefits and drawbacks, oversampling vs non oversampling DAC comparison, and the rest.
Why do you need a NOS DAC?
As mentioned earlier, the PCM digital-to-analog converter traditionally contains an oversampled to enable better utilization of the analog filter because the analog filter is a mandatory part of PCM and DSD DAC.
The reason a non oversampling digital-to-analog converter exists is for the elimination of oversampling artifacts ( distortions, digital filter ringing, and unflat amplitude-frequency response within the filter’s passband region, plus phase shifts in some cases). It would be everything a DAC is, but with no oversampled module and a digital filter.
Advantages and disadvantages of Non-oversampling DACS
Let’s digress for a moment to analyze some advantages and disadvantages of non oversampling DACS.
It is a known fact that non oversampling DACs are very well accepted by audiophiles and, as we’ve spoken with some of them, the explanation they provided to us is that NOS DACs are smoother and more natural in their presentation. Due to their peculiar sound traits and their perceived advantages.
The following outlines some important advantages and disadvantages related to NOS DACs:
Advantages of non oversampling (NOS) DACs
Natural and Organic Sound
The sound reproduction capabilities of NOS DACs, such, smooth, warm, lifelike, and natural (un-digital” like), is often regarded as preferred. Many audiophiles attribute this to his overpowering dominant nature.
Minimal Processing Artifacts
Not oversampling and not using digital filters gives address to problems with pre-ringing and phase distortion typically found in other products; NOS DACs preserve the undistorted and unblemished audio signal.
Simpler Circuit Design
With fewer components within the NOS DACs, they possess a more uncomplicated electronics, aiding to electronic noise and clearer signal path.
Analog Emphasis
Reliance supports the use of analog filtering instead of digital processing, which sits well with purists who appreciate the qualities of analog sound.
Lower Latency
Less delay without oversampling is another factor that favors some applications involving NOS DACs.
Retro Appeal
NOS DACs are often found in vintage and DIY audio products catering to those fond of a minimalistic and old-fashioned style.
Nonsurpassing DACs are more effective in power consumption, which leads to lower power requirements because they do not do any complex digital processing.
Disadvantages of Non-Oversampling DACs
Limited High Frequency Response
Audio fidelity may decrease due to the loss of detail in oversampled output signals for higher frequencies.
Aliasing Risk
Drawing no digital filters allows the possibility of aliasing artifacts being rendered audible, especially at higher volumes.
Restricted Versatility
Modern streaming technologies or high-resolution audio formats might make it difficult for NOS DACs to oversample.
Analog Filter Reliance
Implementation and design issues with analog filters may lead to significant sound quality problems.
Initial Stepped
Rather than being smooth, the first output from a NOS DAC is “stepped”, and with the amount of smoothing required, precision becomes questionable.
A Small Section of Appeal
Allocate audiophiles a specific subset of needs with NOS DACs, manufacturers users who prefer technical perfection or advanced audio formats do not.
Sound Quality Subjectively
The ‘organic’ sound might be appealing to some, while others expect more detail and nuance from oversampling models.
non oversampling DAC and upsampling
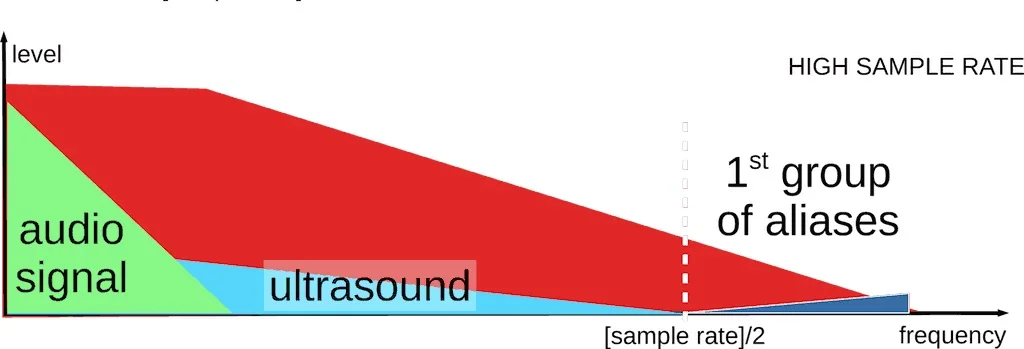
In reality, the number of sampling rates available for purchase or CD ripping is limited. To enable playback on a NOS DAC, these audio files need to be upsampled digitally to a compatible level for playback.
Even with a basic personal computer or a laptop, resampling can be done, and many insert additional peripherals that allow them to edit the audio signal more precisely. However, the quality of audio is determined not only by available resources. Because resampling filters can be implemented in different ways.
Why Filters Matter in Converting Data to Analog Signals
Filters are extremely important in the conversion process as they help in changing the electrical impulses used to capture and reproduce audio into sound waveforms. This is over other functions performed by the filter, which include removing or cleaning traces of artifacts put in place in the previous processing stages of the NOS DAC filter, carving out the band needed to work on the aliasing noise and high-frequency clutter.
In essence, digital filters must be analyzed for their roll-off and filter order. Roll-off is best defined in terms of a rate-control feature indicating how fast or how slow the filters cut back on frequencies above the set limit. Accordingly, filters having a steep roll-off slope must be beneficial in cutting aliased distortion but will be adverse to high-frequency content.
The Effect of Different Digital Filter Types on the Sound Produced by NOS DACs
In non oversampling (NOS) DACs, simplicity is prioritized, and digital filters are usually omitted, leaving only analog filters to manage the processing that follows the conversion. However, in cases where digital filters are included, for example, hybrid NOS designs, the filter type used can have a major impact on the sound signature. Let me illustrate how different types of digital filters can influence the sound of NOS DACs.
1. Linear Phase Filters
Features:
Linear phase filters deliver a phase-intact accuracy, meaning all frequency signals will be uniformly delayed for the same duration during processing.
Sound Impact:
Sharp and clean imaging and accurate reproduction of the sound stage.
Pre-ringing, which is widely regarded as unnatural (especially during transients), will be introduced, such as percussion sounds.
Most Common use:
This is rare to find in NOS DACs as they don’t adhere to the purist approach. These are, however, sometimes integrated into hybrid designs.
2. Minimum Phase Filters
Characteristics:
Filters that eliminate pre-ringing fully offset it, allowing some non-linear phase distortion.
Sound Impact:
Presents more genuine dynamics and rich timbres.
Limited Spherical (or spatial) cues distortion due to phase shifts does impact the soundstage.
Most Common use:
These are commonly used in designs aiming to deliver performance and natural sound for the two paired together harmoniously.
3. Slow Roll-Off Filters
Characteristics:
Slow roll-off filters are softer on the frequency cut-off, allowing some high frequencies and even aliasing to pass through.
Sound Impact:
Sounds warmer and more analog.
Preserves less of the high-frequency detail, which tends to soften the overall presentation.
Common Use:
Often associated with NOS due to the smooth and relaxed sound.
4. Fast Roll-Off Filters
Characteristics:
These filters possess a steep frequency cut-off, which suppresses high-frequency artifacts like aliasing.
Sound Impact:
Accurate and detailed reproduction of sound without distortion.
To some, it can be overly analytical or harsh.
Common Use:
Rarely used in NOS DACs because of the more digital-sounding character.
5. No Digital Filter (True NOS)
Characteristics:
True NOS DACs do not apply digital filters and thus, all processing that occurs after conversion is done in the analog domain.
Sound Impact:
Delivers pure, unprocessed signal, providing a raw and organic listening experience.
Can suffer from aliasing and frequency roll-off, especially at the high-end.
Common Use:
Central to the philosophy of traditional NOS DACs.
Summary of Impact on NOS DAC Sound
Filtered NOS DACs: add a blend of digital and analog features, providing an adjustable sound signature, like employing minimum phase or slow roll-off filters for warmth.
Unfiltered NOS DACs: Bring forth the unNOSed philosophy by providing the cleanest implementation of NOS. It preserves the analog silky smoothness at the expense of possible aliasing and roll-off at high frequencies.
Filters Selection Made Simple
In an NOS DAC, the choice of the filter (or lack of it) is dependent on the listener’s preference:
Balanced Dynamics: A minimum-phase filter should be considered.
Natural and Analog Sound: Digital filters that are off or no filters at all should be used.
Technical Precision: A Fast roll-off or a linear phase filter should be used.
Pros and Cons of non oversampling DAC
Pros of non oversampling (NOS) DACs
- Artifact Free
- Minimal Parts
- No Delays
- Reduced Power
- Straightforward
- Analog Heavy
- Unique Experience
Cons of non oversampling (NOS) DACs
- Shrinking High Frequencies
- Participants
- Middle of the Road
- Overreliance on Analog Filtering
Comparing non oversampling (NOS) and Oversampling DAC Architectures
When basing the decision on whether to go for NOS or oversampling DACs, be sure to familiarize yourself with their architectural differences, as well as their consequences to the quality of sound, design, and ease of use. Here’s a more in-depth breakdown:
- Approach towards processing Signals
NOS DACs: Port the digits into an analog signal directly without upsampling or adding details.
There are no digital filters, it depends on the post filter smoothing done by analog filters.
Strives to maintain the signal in its raw, untouched form.
Oversampling DACs:
They increase the sample rate by adding interpolated data points, which is always up for debate.
These use digital filters to suppress aliasing and improve the performance of high frequencies.
Outputs a smoother and more detailed signal.
- Sound Characteristics
NOS DACs:
Warmth and natural tone, like hearing something on an old tape deck.
“Gray” area, aliasing high-frequency rolloff artifacts may occur.
Minimal appeal to the more ’purist’ crowd. No unnecessary shaping was done.
Oversampling DACs:
Very crisp, precise, and detailed sound. High-frequency response provides clarity.
Able to create digital artifacts pre-ring and phase distortion.
Have the strongest reputation for being too ‘clinical’.
- Design Complexity
NOS DACs:
Easy design. Fewer components and processing stages.
Simplistic mechanical and analog designs, like bespoke filters and then delicate power supplies.
Much more appealing to the purist DIY crowd.
Oversampling DACs:
Additional stages of digital signal processing create more complex implementations.
Requires high precision engineering, as advanced digital filters must be expertly designed for custom algorithms that interpolate in real time.
- Performance and Compatibility
NOS DACs:
Rely upon the bit depth and the original sample rate of the input signal.
Not convenient with more modern audio with high-resolution formats.
Do not cope well with ultra-high sample rates or modern streaming services.
Oversampling DACs:
Excellent compatibility with high-res DSD audio or 24-bit/192 kHz PCM.
Handle complex audio files with high sample rates without distortion much better.
- Filtering and Noise Management
NOS DACs:
All rely on analog-based filters for post output smoothing. They won’t do a better job on suppressing aliased signals.
If the design isn’t well thought out, high-frequency noise may be added.
Oversampling DACs:
Filters manage most aliasing noise.
Separate analog filters are often less complex and less important.
- Power Consumption
NOS DACs:
Power is not wasted on oversampling and other digital functions, resulting in lower power requirements.
Oversampling DACs:
Consistently use power because of extensive digital signal processing.
- Target Audience
NOS DACs:
Simplistic design, minimal sound processing, and no alteration of the signal appeal to audiophiles.
They are popular among those who have vintage audio setups or eclectic systems.
Oversampling DACs:
Multifunctional and modern format versatility appeals to those needing precise detail and sharp image clarity out of traditional audio components.
They are widely used in professional and consumer audio systems.
Summary Table
| Feature | NOS DACs | Oversampling DACs |
|---|---|---|
| Signal Path | Direct conversion, no oversampling | Upsampling with digital filtering |
| Sound | Warm, organic, natural | Detailed, precise, analytical |
| Design | Simple, minimalistic | Complex, technology-driven |
| Compatibility | Limited to standard resolutions | Compatible with high-res formats |
| Filtering | Relies on analog filters | Uses digital filters |
| Noise Handling | Potential for aliasing artifacts | Suppresses noise effectively |
| Power Consumption | Low | Higher |
| Audience | Purists, vintage enthusiasts | High-res audio enthusiasts |
Which is Right for You?
Select NOS DACs if you:
Want a warmer and more realistic-sounding audio experience?
Appreciate simplicity and the beauty of analog.
Do not need support for high-res audio and other advanced formats.
Choose Oversampling DACs if you:
Want accuracy, clarity, and support for modernized formats.
Whether it’s for home theaters or casual listening, have more versatility in devices/brands used.
Value and prioritize technical precision over subjective warmth and softness.
Both approaches have their pros and cons, which implies that your listening habits and requirements will determine the best choice.
Verdict
Last but not least let’s make sure to clarify that audio is a very subjective matter, so choosing between NOS and oversampling DACs is fully dependent on the type of sound signature you’re after.
One piece of advice I would offer would be starting with an open-minded approach toward NOS DACs. Experiment with different configurations because what works best for others’ audiophile expectations might not do the same for you.
For any further queries or questions, feel free to reach out.


